- The objective of wafer cleaning and surface conditioning is the removal of particle and chemical impurities from the semiconductor surface without damaging or deleteriously altering the substrate surface. 晶圆清洗和表面处理的目标是去除半导体表面的颗粒和化学杂质,同时不损坏或恶化基底表面。
- Most wet processes in wafer fab involve cleaning of wafer surfaces. Some of these cleans also involve etching. 晶圆厂中的大多数湿法工艺涉及晶圆表面的清洗。其中一些清洗过程还包括蚀刻。
- The number of cleaning steps in a process flow is typically 20-25% of the total steps in the process and involve all parts of the flow. At 0.18-micron design rules, 80 out of ~400 total steps will be cleaning. 在工艺流程中,清洗步骤通常占总步骤的 20-25%,并涉及整个流程。在 0.18 微米设计规则下,大约 400 个总步骤中有 80 个用于清洗。
- Cleans typically precede all diffusion steps and film deposition steps, and they follow all RIE or plasma etch steps and plasma strip processes. 清洗通常发生在所有扩散步骤和薄膜沉积步骤之前,并且在所有 RIE 或等离子刻蚀步骤以及等离子去胶工艺之后进行。
Wafer Processing Requires Cleaning
![[Pasted image 20250423000405.png#pic_75center|]]
- Oxidation (Field oxide)
- Photoresist strip
- Oxidation (Gate oxide)
- Polysilicon Deposition
- Ion Implantation
- Active Regions
- Nitride Deposition
- Contact Etch
- Metal Deposition and Etch
Types of Contamination
![[Pasted image 20250423001039.png#pic_75center|]]
- Particles
- Metallic Impurities
- Organic Contamination
- Native Oxides wafer在自然环境下自己会氧化
- Electrostatic Discharge
可以忽略
Adhesion of Particles to Surfaces
- Attractive Forces (AF)
吸引力
- van der Waals forces (short range) 范德华力,分子间作用力,作用范围短
- Electrostatic (if the charge on the particles is opposite to the charge on the surface (typically longer range) 静电,作用范围长
- Repulsive Forces (RF)
斥力
- Electrostatic (charge on the particle has the same sign as that on the surface) 静电作用(颗粒上的电荷与表面上的电荷符号相同)
- Steric forces (due to absorbed polymer layers on the surface of the particles and wafer) (short range) 位阻力(由于颗粒和晶圆表面吸附的聚合物层造成的)(短程作用)
When AF > RF, particle deposition is favorable 当粘附力(AF)大于排斥力(RF)时,颗粒沉积是有利的。
- Development of surface charge
表面电荷的形成
- Adsorption of H+ and OH- ions (oxides) 吸附 H+ 和 OH- 离子(氧化物)
- Selective adsorption of positive or negative ions (hydrophobic materials) 选择性吸附正离子或负离子(疏水性材料)
- Ionization of surface groups (polymers such as nylon) 表面基团的离子化(如尼龙等聚合物)
- Fixed charges in the matrix structure exposed due to counter ion release
由于反离子释放,基质结构中暴露的固定电荷
- example: positively charged modified filters used in DI water purification 示例:用于去离子(DI)水净化的带正电荷的改性过滤器
Particle
-
Causing Defects in Lithography Patterns 导致光刻图案缺陷
-
Particle sources:
- air
- people
- A typical person emits 5-10 million particles per minute.
- equipment
- chemicals.
Particle density (number/ml) for ULSI grade chemicals
Metal
![[Pasted image 20250423002457.png#pic_75center|]]
- Heavy Metal一般是在金属沉积阶段引入的,金属接触、互联,尤其是Al
- Alkali Metal在化学处理中产生
Native Oxide
- Native oxide lines the bottom of the contact hole, creating poor electrical contact between tungsten and the doped silicon region. Native Oxide覆盖了过孔的底部,导致钨与掺杂区域之间的接触较差。
![[Pasted image 20250423002737.png#pic_75center|]]
在互联之前,沟道或者过孔会暴露。然后这个新鲜的硅会产生氧化硅绝缘层,导致无法形成有效的金属接触。
Clean Factory: the First Approach Against Contamination
- Modern IC factories employ a three tiered approach to control unwanted impurities:
- clean factories
- wafer cleaning
- gettering
Clean Room
- Factory environment is cleaned by:
- HEPA filters and recirculation for the air.
空气的 HEPA 过滤和循环
- HEPA: High Efficiency Particulate Air
- HEPA filters composed of thin porous sheets of ultrafine glass fibers (
diameter). HEPA 过滤器由超细玻璃纤维的薄孔隙片组成(纤维直径小于 )。 - It is 99.97% efficient at removing particles from air. 过滤效率高达 99.97%,能够去除空气中的微粒
- Room air forced through the filter at 50cm/sec. 室内空气以 50cm/sec 的速度强制通过过滤器
- Large particles trapped, small ones stick to the fibers due to electrostatic forces. 大颗粒被捕获,小颗粒则因静电力附着在过滤纤维上
- The exit air is typically better than class 1. 过滤后的空气通常优于 Class 1 级别
- “Bunny suits” for workers. 工作人员穿着“兔子服”
- Filtration of chemicals and gases. 化学物质与气体的过滤
- Manufacturing protocols. 制造流程的控制与管理
- HEPA filters and recirculation for the air.
空气的 HEPA 过滤和循环
Class
![[Pasted image 20250425183525.png#pic_75center|]]
-
Air quality is measured by the “class” of the facility.
-
Class 1-100,000 mean number of particles, greater than
, in a cubit foot of air (1 foot is 0.3048 meters). 等级 1-100,000代表每立方英尺空气中大于 的颗粒数量。(1 英尺 = 0.3048 米) -
A typical office building is about class 100,000. 典型的办公楼约为100000
-
The particle size that is of most concern is
. Particles tend to coagulate into large ones; those are heavy and precipitate quickly. 微粒中最需要考虑的是尺寸位于 之间的。小于 的微粒容易凝聚成较大的,大于 的很重,很快沉降 -
Particles deposit on surfaces by:
- Brownian motion (most important for those
) - gravitational sedimentation (for larger ones) 微粒沉积在表面的作用有:
- 布朗运动(对于小于
的微粒) - 重力沉降(对更大的)
- Brownian motion (most important for those
Modern Wafer Cleaning
-
Cleaning involves removing particles, organics and metals from wafer surfaces. 清洁过程包括去除晶圆表面的颗粒、有机物和金属
- Particles are largely removed by ultrasonic agitation during cleaning. 颗粒主要通过超声振动清洗去除
- Organics (photoresist) are removed in
plasma or in (Piranha) solutions. 有机物(光刻胶)可通过 等离子体或 (Piranha 溶液)去除 - The “RCA clean” is used to remove metals and any remaining organics. “RCA 清洗”用于去除金属及剩余的有机物
-
Typical person emit 5-10 million particle per minute. Most modern IC plants use robots for wafer handling. 典型的人每分钟释放 500-1000 万个颗粒。大多数现代集成电路(IC)工厂采用机器人进行晶圆处理。
Typical Wafer Wet-Cleaning Sequence
![[Pasted image 20250425184238.png#pic_75center|]]
Wet-Cleaning Chemicals (Organics)
- PIRANHA or SPM (Sulfuric Acid-Hydrogen Peroxide)
- Sulfuric acid/hydrogen peroxide/ deionized water (SPM,
) 硫酸/过氧化氢/去离子水 - Temperature range of 110-130°C 温度范围:110-130°C
(98%) and (30%) in different ratios 硫酸(98%)和过氧化氢(30%)按照不同的比例混合 - Used for removing organic contaminants and stripping photoresists 用于去除有机污染物及剥离光刻胶
- Will grow an oxide on bare silicon but will not grow oxide on oxidized surfaces 可在裸硅表面生成氧化层,但不会在已氧化的表面上生成氧化层
- Peroxide has a limited lifetime, replenished by spiking with added peroxide 过氧化氢的寿命有限,可通过补充过氧化氢延长
- Sulfuric acid/hydrogen peroxide/ deionized water (SPM,
- Sulfuric acid disadvantages
硫酸的缺点
- Difficult to remove from surfaces 难以从表面去除
- Water used for rinsing is usually very hot 冲洗的水通常非常热
- Amount of sulfur left on surfaces is very high. 表面残留的硫元素含量较高
- Removed easily with a brief HF dip 可通过短暂的 HF 浸泡轻松去除
Wet-Cleaning Chemicals (Oxides)
- DHF
DHF(稀释氢氟酸)
- Hydrofluoric acid or diluted hydrofluoric acid (HF or DHF @
). 氢氟酸或稀释氢氟酸(HF 或 DHF,温度 ) - Removes oxides from area of interest, etches silicon oxides and dioxides. 去除目标区域的氧化物,蚀刻硅氧化物和二氧化硅
- Reduces metals contamination of the surface. 降低表面上的金属污染
- Sometimes buffered oxide etch(BOE or BHF,
@ Room temperature) is used in place of DHF in some processes, but may lead to precipitation and contamination. 某些工艺中,缓冲氧化蚀刻(BOE 或 BHF, ,室温)可替代 DHF,但可能导致 沉淀和污染
- Hydrofluoric acid or diluted hydrofluoric acid (HF or DHF @
Wet-Cleaning Chemicals (Particles)
![]()
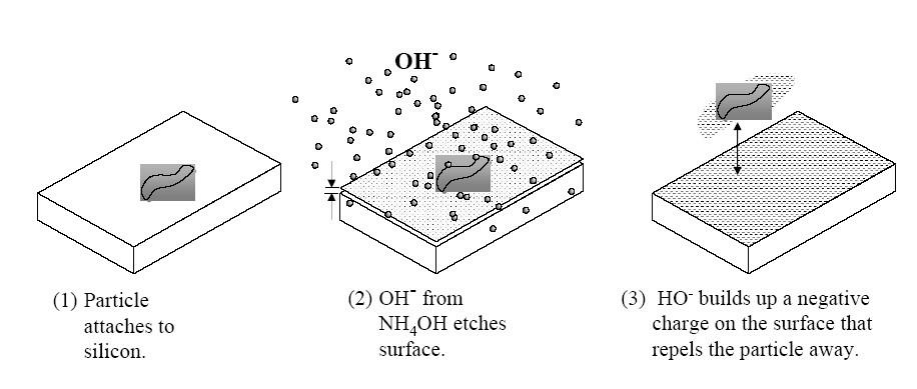
- APM (SC-1):
APM(SC-1):氨水-过氧化氢溶液 - Ammonium hydroxide/hydrogen peroxide/DI water mixture (
). 氢氧化铵/过氧化氢/去离子水混合物( ) - Temperature range of 60-80°C 温度范围:60-80°C
- Standard solution is
标准溶液比例: - APM oxidizes the bare silicon to form native (chemical) oxide APM 氧化裸硅,形成自然的(化学)氧化物
- slightly etches oxides at a low rate (~1Å/min) and can etch silicon 以较低速率蚀刻氧化物(约 1Å/分钟),同时可蚀刻硅
- slightly etches to undercut and remove particles from the surface 轻微蚀刻以削弱颗粒附着力并将其从表面去除
- Typically used for particle removal. 主要用于颗粒去除
- it also removes organic and metal contaminants. 还可去除有机污染物和金属污染物
- Ammonium hydroxide/hydrogen peroxide/DI water mixture (
- Problems
- Can also result in surface roughening 可能导致表面粗糙
- Presence of the oxidant is critical. If lost, solution will etch silicon. 氧化剂的存在至关重要,若无,溶液将蚀刻硅
Wet-Cleaning Chemicals (Metals)
- HPM (SC-2)
- Hydrochloric acid/hydrogen peroxide/DI water (HPM,
(1:1:5) @ ) 盐酸/过氧化氢/去离子水(HPM, (1:1:5), ) - Temperature range of 60-80°C
- Standard solution is
= 1:1:5 - HPM removes metallic contaminants from substrate and acts as oxidizing agent. HPM 可去除衬底上的金属污染物,并具有氧化剂作用
- Mechanism for operation: chlorides of most metallic contaminants are soluble in an acidic solution 作用机制:大多数金属污染物的氯化物在酸性溶液中可溶解
- Peroxide may not be needed at low metallic contamination levels. 当金属污染水平较低时,可能无需添加过氧化氢
- Hydrochloric acid/hydrogen peroxide/DI water (HPM,
Wet-Cleaning Chemicals (DI water)
- UPW as Processing Chemical
- Ultra-pure water (UPW). Commonly called as DI water. 超纯水(UPW),通常称为去离子水(DI 水)
- Most heavily used chemical in wafer fabrication > 6000 gal/8”CMOS wafer. 晶圆制造过程中使用最广泛的化学品,每生产一片 8 英寸 CMOS 晶圆需消耗超过 6000 加仑(gal)水
- it dilutes chemicals and rinses solutions after chemical cleans. 用于稀释化学品并在化学清洗后冲洗溶液
- Rinse multiple times until solution reaches high resistivity in given time period 需要多次冲洗,直至溶液在规定时间内达到高电阻率
- DI water must be manufactured on site to achieve the quality and purity levels required by modern microfabrication. DI 水必须在工厂现场制造,以满足现代微制造所需的质量和纯度标准
- Each gallon of DI water may require as much as 4-6 gallons of raw city grade water to manufacture. 每生产一加仑 DI 水可能需要消耗 4-6 加仑的原始市政级水
- DI water must be continuously recirculated in order to achieve the quality and purity levels. DI 水必须持续循环,以确保其质量和纯度
Typical UPW System
![[Pasted image 20250425185820.png#pic_50center|]] ![[Pasted image 20250425185826.png#pic_50center|]]
Cleaning for Advanced Wafer Processing
- Front-End-Of-Line (FEOL) Individual devices are patterned in the semiconductor wafer
晶圆上单个器件光刻后
- Pre-Diffusion Cleaning 扩散前清洗
- Post Photolithography Photoresist Removal and Cleaning 光刻后光刻胶去除及清洗
- Post Gate Etch Photoresist Removal and Cleaning 栅极蚀刻后光刻胶去除及清洗
- Post Ion Implant Photoresist Removal and Cleaning 离子注入后光刻胶去除及清洗
- Post Shallow Trench Isolation (STI) CMP Cleaning 浅沟槽隔离(STI)化学机械抛光(CMP)清洗
- Back-End-Of-Line (BEOL) Individual devices are interconnected with wiring on the wafer
在晶圆上通过布线互连单个器件后
- Pre Thin-Film Deposition Cleaning 薄膜沉积前清洗
- Post Contact and Via Etching Cleaning 接触孔及通孔蚀刻后清洗
- Post Metal Etching Photoresist Removal and Cleaning 金属蚀刻后光刻胶去除及清洗
- Post Metal and Low-k Dielectric CMP Cleaning 金属及低介电常数材料的化学机械抛光(CMP)清洗
Pre-Diffusion Clean
- Cleans before furnace operations are critical
- Defects or contamination will be incorporated into the wafer if not removed prior to high temperature furnace operation 如果在高温炉操作前未去除缺陷或污染物,这些杂质会被晶圆吸收
- Most important steps - those where bare silicon is present
- Pre-initial
- Pre-gate
- Typically full cleans (Piranha+BOE (Buffered Oxide Etch, HF) +SC (standard clean) 1+SC2)
Solvent Based Cleaning (Post-Etch and BEOL)
- Mainly used for Post-Etch Cleaning to remove phtoresist and etch residues. For BEOL cleaning in the presence of metal layers
主要用于蚀刻后清洗,以去除光刻胶和蚀刻残留物。BEOL:金属层布线后清洗
- Resist strippers - proprietary mixtures of organic solvents and active ingredients
光刻胶去除剂——专有混合物,包含有机溶剂和活性成分
- The solvents are typically NMP (N-methyl pyrrolidone) 典型溶剂为 NMP(N-甲基吡咯烷酮)
- NMP is water soluble and neutral in aqueous solution NMP 可溶于水,在水溶液中呈中性
- “Active ingredients” are typically amines “活性成分”通常为胺类化合物
- Attack the resist and dissolve into the solvent media. 可破坏光刻胶并溶解至溶剂介质中
- New strippers - “semi-aqueous”, containing both organic solvents and water along with “active ingredients” and corrosion inhibitors 新型去除剂——“半水基”,含有机溶剂、水、活性成分及防腐剂
- Resist strippers - proprietary mixtures of organic solvents and active ingredients
光刻胶去除剂——专有混合物,包含有机溶剂和活性成分
Resist Strip
- Resist removed by ashing - a plasma process which “burns” the resist off the surface (Note - Resist contains measurable amounts of impurities, such as sodium.) 通过Ashing去除光刻胶——一种等离子体工艺,可将光刻胶从表面“烧除”(注意:光刻胶含有可测量的杂质,如钠)
- Ashing concentrates impurities on the surface.
Ashing会使杂质集中于表面
- Must be followed by a wet process to remove contaminants 必须后续采用湿法工艺去除污染物
- Sulfuric acid-hydrogen peroxide used before metal is present on the wafer (FEOL) 在金属未沉积于晶圆表面之前(FEOL),使用硫酸-过氧化氢溶液
- Solvent strippers used after metal deposition (BEOL) 在金属沉积之后(BEOL),使用溶剂型去除剂
Post-Etch Clean
- Reactive ion etching (RIE) = a physical-chemical process which can leave residues (or polymer) 反应离子刻蚀(RIE)是一种物理-化学过程,可能会留下残留物(或聚合物)
- RIE uses chemically reactive plasma to remove material deposited on wafers. The plasma is generated under low pressure (vacuum) by an electromagnetic field. High-energy ions from the plasma attack the wafer surface and react with it. RIE 通过化学活性等离子体去除沉积在晶圆上的材料。等离子体在低压(真空)下由电磁场产生,高能离子从等离子体中释放,并与晶圆表面发生反应
- Difficult to remove (can be fluorinated polymers) so both ash and wet clean are usually used
残留物难以去除(可能是含氟聚合物),因此通常同时使用Ash和湿法清洗
- Residues are created to inhibit attack of the plasma on the sidewall of the etched film 残留物用于抑制等离子体对刻蚀膜侧壁的蚀刻
- Changes in the etch process or the material being etched can require changes in the clean 刻蚀工艺或刻蚀材料的变化可能需要调整清洗方法
- Solvent based cleanings are required for different post etch cleaning process 不同的Post-Etching清洗工艺需要使用溶剂清洗
Post-Etch Residues from RIE Processes
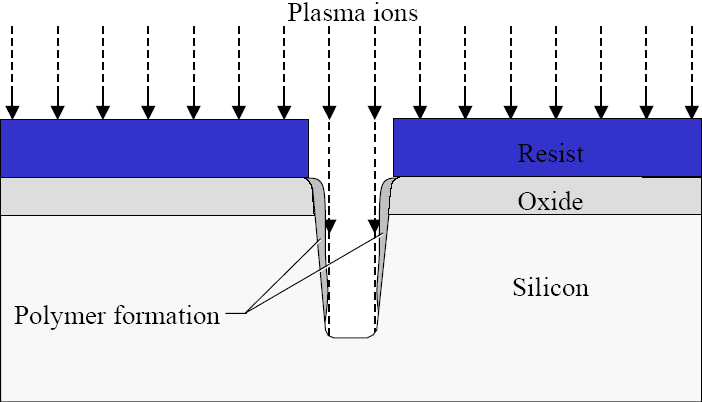
![[Pasted image 20250425191129.png#pic_75center|]]
- Post Etch Residue on sidewall of etch pattern 刻蚀后残留物:刻蚀图案侧壁上的残留物
- Post Ash Residue: residue(Veils) on sidewall of pattern after plasma ashing to remove the bulk of photoresist 灰化后残留物:在等离子灰化去除大部分光刻胶后,图案侧壁上的残留物(Veils)
Post-Etch Residues Clean
![[Pasted image 20250425191400.png#pic_75center|]]
Wet-Cleaning Equipment
- 超声波清洗(Megasonics)
- 喷雾清洗(Spray Cleaning)
- 擦洗器(Scrubbers)
- 晶圆冲洗(Wafer Rinse)
- Overflow Rinsers 溢流
- Dump Rinse 倾倒
- Spray Rinse 喷雾
- Hot DI-Water Rinsing 热去离子水
- Wafer Drying
- Spin Dryers 旋转
- IPA Vapor Dry IPA(异丙醇)蒸汽
Megasonic Cleaning
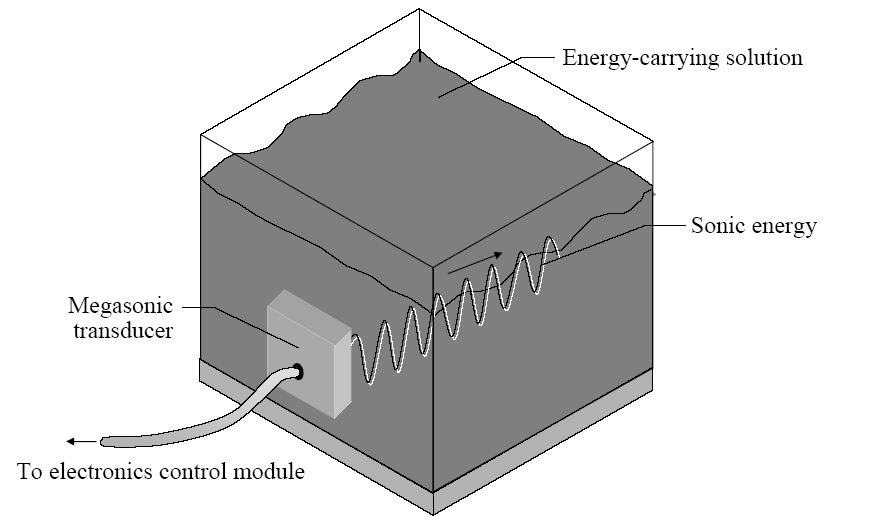
- Megasonic agitation is the most widely used approach to adding energy (at about 800kHz and 100,000g) to the wet cleaning process. 兆声振动(Megasonic agitation)是湿法清洗过程中最常用的能量增强方法,工作频率约为 800kHz,产生约 100,000g 的加速度。
Post-CMP Scrubbing
![[Pasted image 20250425191659.png#pic_75center|]]
Water Rinsing
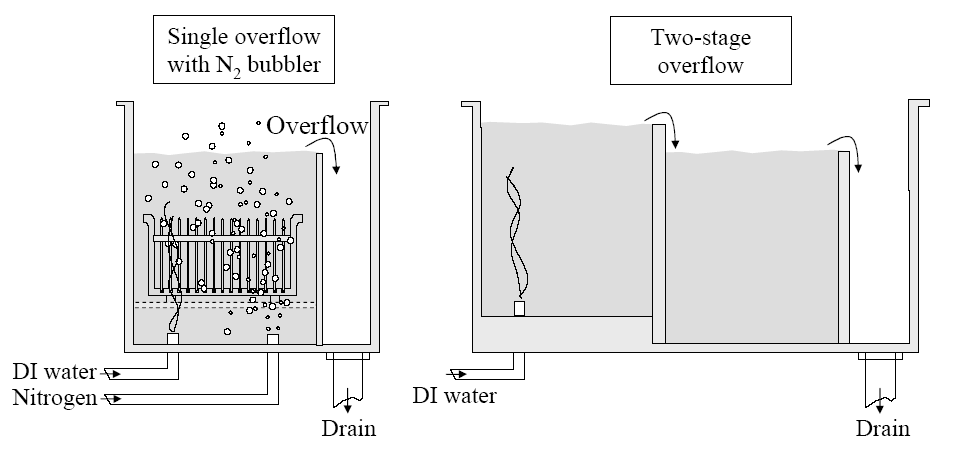
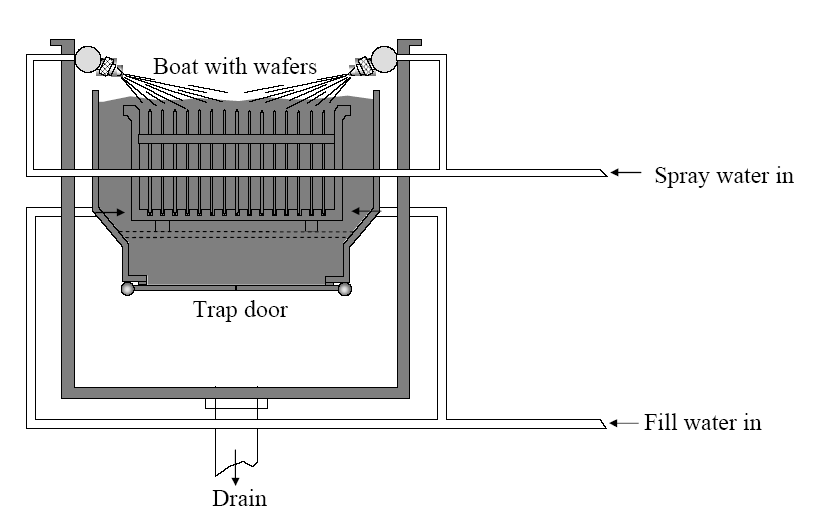
-
When overflow is complete, the bottom quick dump door opens and the rinse water drains from the tank in a matter of seconds while nozzle sprayers on the top of tank keep the product wet with fresh, clean DI water during the dumping process. 当Overflow过程完成后,底部的快速倾倒门打开,冲洗水在几秒钟内从水箱中排出。同时,水箱顶部的喷嘴喷雾装置在倾倒过程中持续用新鲜、洁净的去离子水(DI 水)保持产品湿润。
-
Continuous flow of water passing through wafer surface 连续水流通过晶圆表面
-
Completion of rinse is determined by measuring the resistivity of the water 冲洗过程的完成由水的电阻率测量来确定
- (Resistivity = very sensitive method of determining the presence of ions in solution) 电阻率是检测溶液中离子存在的一种非常灵敏的方法
-
Dump rinsing - used for wafers that are hydrophilic 用于亲水性的晶圆
-
Hot water - used after some processes (but not HF treated surfaces) 适用于某些工艺后的处理(但不适用于 HF 处理过的表面)
Drying
- Critical step in cleaning
- Objective - remove as much of the water as possible before it can dry on the surface and leave residues from any impurities in the water 目标:尽可能去除水分,以防其在表面干燥后留下水中杂质的残留物
- Two types of dryers
- Spin rinse dryer (SRD) - throw off as much water as possible 尽可能甩掉水分
- IPA vapor - displace water with IPA
通过 IPA 置换水分
- IPA vapor dryer styles
- Tank 水槽
- Vapor jet (VJD) 蒸汽喷射
- Marangoni-type
- IPA vapor dryer styles
![[Pasted image 20250425192102.png#pic_50center|]]
- wafers put into a cassette and the cassette rotates at few thousand RPM 晶圆被放入晶圆盒中,并以几千转每分钟(RPM)旋转
- throw off as much water as possible 尽可能甩掉水分
- Hot
purge helps to dry wafer faster 热氮气( )吹扫有助于加快晶圆干燥速度
Marangoni Wafer Drying in IPA ambient after cleaning
![[Pasted image 20250425192307.png#pic_75center|]]
- The Marangoni principle involves the slow withdrawal of wafers from a DI water bath(or DI water level moving down the wafer surface) to an environment of isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and nitrogen such that only the portion of the surface that is at the interface of the liquid and vapor phases is “drying” at any one time. Marangoni 原理涉及将晶圆从去离子水(DI 水)浴中缓慢取出(或 DI 水位沿晶圆表面下降),进入异丙醇(IPA)和氮气环境,使得在液相和气相界面处的表面部分在任何时刻仅逐步“干燥”。
![[Pasted image 20250425192405.png#pic_50center|]]
- A low concentration of IPA vapor condenses on the water surface. 低浓度的 IPA 蒸汽在水表面凝结
- As the wafers are withdrawn slowly from the water, the IPA layer displaces the water. The IPA evaporates from the wafers and they are dried. 当晶圆缓慢从水中取出时,IPA 层置换水分。IPA 从晶圆表面蒸发,使其干燥
![[Pasted image 20250425192516.png#pic_75center|]]
-
旋转冲洗干燥器(SRD): 晶圆在高速旋转的盒子中旋转,通过离心力去除水分。
- 优点:
- 资本成本低
- 不消耗IPA
- 缺点:
- 可能产生水印
- 通孔可能保留水分(适用于低技术干燥)
- 机械处理可能偶尔损坏晶圆
- 不能没有盒子
- 优点:
-
IPA蒸汽干燥器: 一个装有液态IPA的腔室被加热。加热与冷却线圈结合使液态IPA形成蒸汽云,晶圆暴露在其中以实现干燥。
- 优点:
- 温和的晶圆处理
- 良好的干燥效果
- 晶圆载体干燥良好
- 与工作台很好地集成
- 缺点:
- 比旋转干燥更贵
- 过程时间比Marangoni长
- IPA消耗量比Marangoni高
- 可用性有限
- 优点:
-
Marangoni干燥器: 浸在水中的晶圆缓慢通过一层薄薄的IPA液体。晶圆利用IPA和水之间的表面张力梯度干燥。
- 优点:
- 温和的晶圆处理
- 被认为是行业中最好的干燥方法,无水印
- 干燥过程中不暴露于空气
- 可进行原位-HF最后一步处理
- 能很好地集成在湿法清洗机内部
- 不需要盒子
- 缺点:
- 成本最高
- 消耗IPA,但用量较少
- 优点: