Introduction to Intrusion Detection
-
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a security mechanism designed to monitor network or system activities for malicious behavior. 入侵检测系统 (IDS) 是一种安全机制,用于监控网络或系统活动以检测恶意行为
-
Advantages of Intrusion Detection Systems
- Early Threat Detection: Identifies suspicious activities before they cause significant damage. 早期威胁检测:在造成重大损害之前识别可疑活动
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuously analyzes system and network activity. 实时监控:持续分析系统和网络活动
- Forensic Analysis: Provides logs and records of attack attempts. 取证分析:提供攻击尝试的日志和记录
- Security Policy Enforcement: Helps organizations comply with security regulations. 安全政策执行:帮助组织遵守安全法规
-
Disadvantages of Intrusion Detection Systems
- False Positives: Anomaly-based IDS may flag normal activity as a threat. False Negatives: Signature-based IDS can miss new, evolving threats. 误报:基于异常的 IDS 可能将正常活动标记为威胁。漏报:基于特征的 IDS 可能漏掉新的、演变中的威胁
- High Resource Consumption: Processing large amounts of traffic requires computing power. 高资源消耗:处理大量流量需要计算能力
- No Active Protection: IDS only detects and alerts; it does not block attacks (IPS does). 无主动保护:IDS 仅检测和报警,无法阻止攻击(IPS 可以)
Types of IDS
- Host-based IDS (HIDS) 基于主机的入侵检测系统 (HIDS)
- Network-based IDS (NIDS) 基于网络的入侵检测系统 (NIDS)
- Distinguished by detection method
- Signature-based IDS: Relies heavily on a predefined set of attack and traffic patterns called signatures. 基于特征的入侵检测系统:主要依赖于一组预定义的攻击和流量模式(称为特征)
- Anomaly-based (heuristic) IDS: Monitors activity and attempts to classify it as either “normal” or “anomalous.” 基于异常(启发式)的入侵检测系统:监控活动并尝试将其分类为“正常”或“异常”
Network-Based IDS
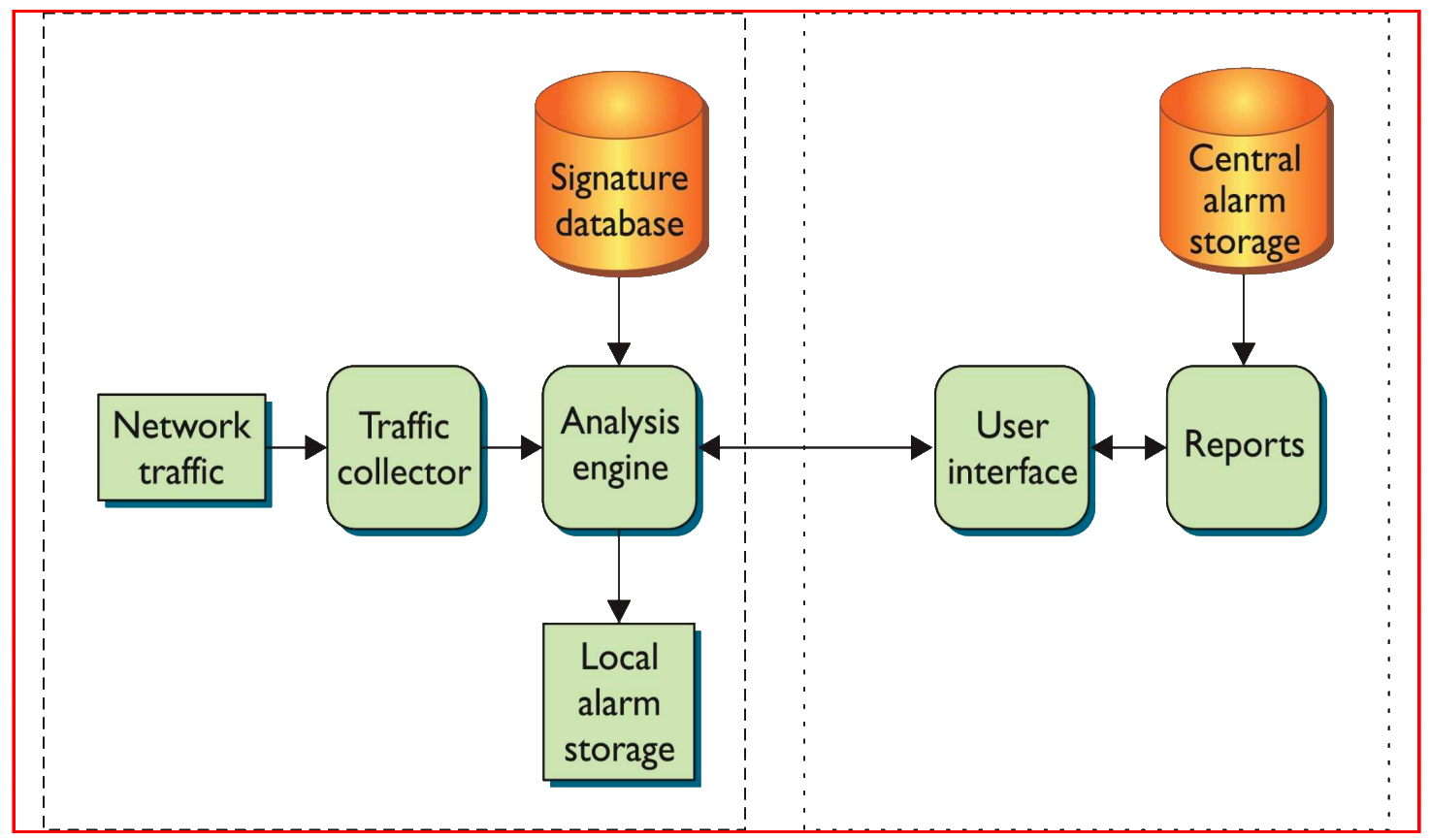
![[Pasted image 20250403195732.png#pic_75center|]]
- Network-Based IDS
- Network-Based IDS (NIDS) are engines that parse network traffic. NIDS 是解析网络流量的引擎
- In addition to capturing all network traffic, NIDS compare the traffic with a set of pre-classified attack signatures. 除了捕获所有网络流量外,NIDS 还将流量与一组预分类的攻击特征进行比较
- Once a signature is found in a network packet, a protective action is launched, and the attack is stopped and logged. 一旦在网络数据包中发现特征,就会采取保护措施,攻击被阻止并记录
- NIDS engines can be easily deployed without suffering major network modifications. NIDS 引擎可以轻松部署,而无需进行重大网络改动
- Advantages of NIDS
- Providing IDS coverage requires fewer systems. 提供 IDS 覆盖所需的系统较少
- Deployment, maintenance, and upgrade costs are usually lower. 部署、维护和升级成本通常较低
- A NIDS has visibility into all network traffic and can correlate attacks among multiple systems. NIDS 能够查看所有网络流量,并可以关联多个系统间的攻击
- Disadvantages of NIDS
- It is ineffective when traffic is encrypted. 在流量加密的情况下无效
- It doesn’t know about activity on the hosts themselves. 无法了解主机本身的活动
Host-Based IDS
![[Pasted image 20250403200352.png#pic_75center|]]
-
Examines activity only on a specific host 仅检查特定主机上的活动
- Examines logs, audit trails, and network traffic coming into or leaving the host 检查日志、审计记录以及进入或离开主机的网络流量
- Examination is done in real time or periodically 检查可实时进行或定期进行
-
Flags that may raise the alarm in a HIDS
- Login failures 登录失败
- Logins at irregular hours 非常规时间的登录
- Privilege escalation 权限提升
- Additions of new user accounts 添加新的用户账户
-
Advantages
- Can be very operating system-specific 非常针对特定的操作系统
- Can reduce false-positive rates 可以降低误报率
- Can examine data after it has been decrypted 可以在数据解密后进行检查
- Can be very application specific 非常针对特定应用
- Can determine how an alarm will impact a system 可以确定警报对系统的影响
-
Disadvantages
- Must process information on every system you want to watch 必须处理您希望监视的每个系统上的信息
- May have a high cost of ownership and maintenance 可能具有较高的拥有和维护成本
- Uses local system resources 使用本地系统资源
-
Passive HIDS
- Watches activity, analyzes it, and generates and alarm 监视活动,分析活动,并生成警报
-
Active HIDS
- Same capabilities as a passive HIDS, with the ability to react to activity by possibly running a script or terminating a process. 拥有与被动型 HIDS 相同的能力,还能够通过运行脚本或终止进程来对活动做出反应
-
Modern HIDS
- Often referred to as host-based intrusion prevention systems (HIPS) and use the following components to prevent attacks
通常被称为基于主机的入侵预防系统 (HIPS),使用以下组件来防止攻击
- Integrated system firewall 集成系统防火墙
- Behavioral- and signature-based IDS 基于行为和特征的 IDS
- Malware detection and prevention 恶意软件检测和预防
- Often referred to as host-based intrusion prevention systems (HIPS) and use the following components to prevent attacks
通常被称为基于主机的入侵预防系统 (HIPS),使用以下组件来防止攻击
Signature-Based IDSs
- It is also known as knowledge-based IDS. 它也被称为基于知识的入侵检测系统 (IDS)
- It examines data traffic looking for something that matches signatures, which are pre-configured, predetermined attack patterns. 它通过检查数据流量,寻找与预配置的、预定攻击模式(特征)匹配的内容
- PROBLEM: Signatures must be continually updated as new attack strategies are identified. 问题:随着新攻击策略的出现,特征必须不断更新
Statistical Anomaly-Based IDSs
- It is also known as behavior-based IDS. 它也被称为基于行为的入侵检测系统 (IDS)
- Collects data from normal traffic and establishes a baseline. 收集正常流量的数据并建立基线
- Once the baseline is established, periodically samples network activity, based on statistical methods, and compares samples to baseline. 一旦建立基线,系统会基于统计方法定期抽样网络活动,并将样本与基线进行比较
- If activity is outside baseline parameters (known as a clipping level), IDS notifies administrator. 如果活动超出基线参数(称为阈值),IDS 会通知管理员
- The system is able to detect new types of attacks as it looks for abnormal activity of any type. 系统能够检测到新类型的攻击,因为它会查找任何类型的异常活动
- Also, may not detect minor changes and can generate many false positives. 但可能无法检测到细微的变化,并且可能会产生许多误报
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
- An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is a proactive security technology that detects and blocks malicious activities in real time. 入侵防御系统 (IPS) 是一种主动的安全技术,能够实时检测和阻止恶意活动
- Unlike Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), which only detect threats and generate alerts, an IPS actively prevents attacks by blocking malicious traffic. 与仅检测威胁并生成警报的入侵检测系统 (IDS) 不同,IPS 可通过阻止恶意流量主动防御攻击
- IPS is often integrated into Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) for advanced network security. IPS 通常集成到下一代防火墙 (NGFW) 中,以提供高级网络安全功能
| Feature | Intrusion Detection System (IDS) | Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects and alerts on threats | Detects and blocks threats |
| Response | Passive (logs & alerts) | Active (prevents attacks in real time) |
| Placement | Monitors network or host activity 监控网络或主机的行为 | Sits inline to inspect traffic before it reaches the system 位于网络流量路径中,在流量到达系统之前对其进行检查 |
| Use Case | Ideal for forensic analysis and monitoring 适合取证分析和监控 | Ideal for real-time security enforcement 适合实时预防 |
| Example Tools | Snort, Zeek, OSSEC | Palo Alto NGFW, Suricata, Cisco Firepower |
Honeypot System
蜜罐系统 ![[Pasted image 20250403202811.png#pic_75center|]]
-
It’s a sacrificial computer system that’s intended to attract cyberattacks, like a decoy. 它是一种牺牲性的计算机系统,旨在吸引网络攻击,就像一个诱饵
-
It mimics a target for hackers, and uses their intrusion attempts to gain information about cybercriminals and the way they are operating or to distract them from other targets. 它模拟黑客的目标,通过他们的入侵尝试获取有关网络犯罪分子及其运作方式的信息,或将其注意力分散到其他目标
-
How Honeypots work
- The honeypot looks like a real computer system, with applications and data, fooling cybercriminals into thinking it’s a legitimate target. 蜜罐看起来像一个真实的计算机系统,带有应用程序和数据,欺骗网络犯罪分子,让他们认为这是一个合法目标
- For example, a honeypot could mimic a company’s customer billing system - a frequent target of attack for criminals who want to find credit card numbers. Once the hackers are in, they can be tracked, and their behavior assessed for clues on how to make the real network more secure. 例如,一个蜜罐可以模拟公司的客户计费系统——犯罪分子经常攻击这种目标以获取信用卡号码。一旦黑客入侵,可以跟踪他们并评估其行为,从中获取线索以增强真实网络的安全性
- Honeypots are made attractive to attackers by building in deliberate security vulnerabilities. 蜜罐通过故意构建安全漏洞使其对攻击者具有吸引力
-
Honeypot security has its limitations as the honeypot cannot detect security breaches in legitimate systems, and it does not always identify the attacker. 蜜罐无法检测合法系统中的安全漏洞。它并不总是能够识别攻击者的身份
Impact of Cyber Security
- More than half of all businesses become a target of a cyber attack every year and it is one of the biggest threats in the cybersecurity world. 超过一半的企业每年都会成为网络攻击的目标,这是网络安全领域最大的威胁之一
- Financial implications. Can cost businesses/individuals anywhere from tens of thousands to millions of dollars and that doesn’t even include the costs associated with recovery. 财务影响:可能使企业或个人损失从几万美元到数百万美元,这还不包括与恢复相关的成本
- Productivity costs. In any business, time is money. A successful attack means significant time lost rectifying the impact of social engineering and resolving the damage. This often affects the IT team’s productivity, general employee productivity, and ultimately, the business’s profitability. 生产力成本:在任何业务中,时间就是金钱。一场成功的攻击意味着花费大量时间来修复社交工程的影响和解决损害问题。这通常会影响 IT 团队的生产力、普通员工的生产力,并最终影响企业的盈利能力
- Operational disruption. Reduced productivity won’t just impact the IT team, it can trickle down to entire supply chain or service delivery operations, slowing every moving part of the business and causing logistical delays. 运营中断:生产力降低不仅会影响 IT 团队,还可能波及整个供应链或服务交付操作,减缓企业的各个环节运转并导致物流延误。
- Reputational damage. Cybersecurity attacks are extremely dangerous, and they put both business and customer information at risk. If an organization is not adequately protected, customers won’t feel safe, and it can be difficult to build back that trust. 声誉损害:网络安全攻击极其危险,会将企业和客户的信息置于风险之中。如果一个组织没有得到充分保护,客户将无法感到安全,并且可能很难重建这种信任。