由于PPT在这里太抽象了先按照原始顺序放着
![[Pasted image 20250402030137.png#pic_75center|]]
-
Greek kryptós (hidden) and gráphien (to write) 希腊词kryptós(隐藏)和gráphien(书写)
-
The study of ways to hide or obscure information, making it unreadable without secret knowledge 研究隐藏或模糊信息的方法,使其在没有秘密知识的情况下无法阅读
-
Cryptography is the use of mathematical operations to protect messages traveling between parties or stored on a computer 密码学利用数学运算来保护双方之间传输的信息或存储在计算机上的信息
-
It involves converting the message from a readable format to non-readable 它包括将信息从可读格式转换为不可读格式
-
It means that someone intercepting your communications cannot read them 这意味着即使有人截获你的通信也无法读取它们
-
It is the science of encrypting and decrypting information to prevent unauthorized access. The decryption process should be known to both the sender and receiver. 密码学是一门加密和解密信息以防止未经授权访问的科学。解密过程应为发送者和接收者双方所知
-
Basic Definitions
- PLAINTEXT: A piece of data that is not encrypted 明文(PLAINTEXT):未加密的数据片段
- CIPHERTEXT: The output of an encryption algorithm 密文(CIPHERTEXT):加密算法的输出
- CIPHER: A cryptographic algorithm 密码(CIPHER):一种密码算法
- KEY: A sequence of characters or bits used by an algorithm to encrypt or decrypt a message 密钥(KEY):用于加密或解密信息的字符序列或位序列
- ENCRYPTION: Changing plaintext to ciphertext 加密(ENCRYPTION):将明文转换为密文
- DECRYPTION: Changing ciphertext to plaintext 解密(DECRYPTION):将密文转换为明文
Application of Cryptography
- There are various applications of cryptography such as:
- WhatsApp Encryption
- Data Security
- Password Security
- Online Communications
- Time Stamping
- End-to-end Encryption
- Online Shopping
- Social Networking
- Online trading
Cryptanalysis
![[Pasted image 20250402122519.png#pic_75center|]]
- It is the process of attempting to break a cryptographic system and return the encrypted message to its original form. 这是试图破解加密系统并将加密信息恢复为原始形式的过程
- The goals of Cryptanalysis is to use various mathematical algorithms to decipher the cipher text. Numerous cryptanalysis attacks are used to achieve this goal. 密码分析的目标是使用各种数学算法来破译密文。为实现这一目标,使用了多种密码分析攻击
Encryption and Decryption Process
![[Pasted image 20250402122639.png#pic_75center|]]
- Notation:
: Message : Ciphertext : Encryption : Decryption (encrypting message = ciphertext) (decrypting ciphertext = message)
Types of Cryptography
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses one key 对称加密:使用一个密钥
- Asymmetric Encryption: Uses two keys 不对称加密:使用两个密钥
- Hashing: No key is used 哈希:不用密钥
Encryption and Decryption Process
![[Pasted image 20250402123322.png#pic_75center|]]
- Notation Using a Key
- Secret-key (Symmetric) Cryptosystem: one key
,
- Public-key (Asymmetric) Cryptosystem: two keys
,
- Secret-key (Symmetric) Cryptosystem: one key
Cryptography
- Cryptographic Algorithms
密码算法
- The cryptographic algorithm, what is commonly called the encryption algorithm or cipher, is made up of mathematical steps for encrypting and decrypting information. 密码算法,通常称为加密算法或密码,包含用于加密和解密信息的数学步骤
- Types of Ciphers
- Substitution ciphers (replace) 替代密码(替换)
- Transposition ciphers (rearrange) 置换密码(重新排列)
- Product ciphers (substitution, permutation, and modular arithmetic) 复合密码(替代、排列和模运算)
- Keys
- Keys are special pieces of data used in both the encryption and decryption processes. 密钥是在加密和解密过程中使用的特殊数据
- The algorithms stay the same, but a different key is used. 算法保持不变,但使用不同的密钥
- The more complex the key, the greater the security of the system. 密钥越复杂,系统的安全性越高
Importance of Key Length
- Key of 8 bits has
or possible combinations. Trivial to break even without a computer (50% chance of finding the key after 128 tries) - Every bit you add, doubles the number of possible combinations.
- Assuming a key of 56 bits, there are
possible combinations. - If a computer can try 1,000,000 keys a second, it would take
years to find the correct key. - A 64-bit key would take 585,000 years.
- 128 bits requires
years - However, computers are much faster than 1M keys/s these days and with hackers using millions of compromised computers in parallel, in reality it is much easy to break it then it is in theory. 然而,现在的计算机速度远快于每秒1百万个密钥,黑客通过并行使用数百万台被攻陷的计算机,在现实中,破解比理论上要容易得多
Cryptography
- Plaintext can be encrypted through bit stream or block cipher method 明文可以通过比特流或块加密方法进行加密
- BIT STREAM: Each plaintext bit transformed into cipher bit one bit (or byte) at a time. RC4 is widely used stream cipher 比特流:每个明文比特逐位(或逐字节)转换为密文比特。RC4是广泛使用的流密码
- BLOCK CIPHER: Message divided into blocks (e.g., sets of 8- or 16-bit blocks) and each is transformed into encrypted block of cipher bits using algorithm and key. DES and AES are block cipher examples.
块加密:将消息分成块(例如,每组8位或16位块),并使用算法和密钥将每个块转换为加密的密文块。DES和AES是块加密的例子
与流密码(Stream Cipher)不同,块密码不会逐位加密,而是一次处理整个数据块。它是现代加密算法中的一个核心组件。
- ENCRYPTION MODES: Different encryption modes may be used. Common modes are:
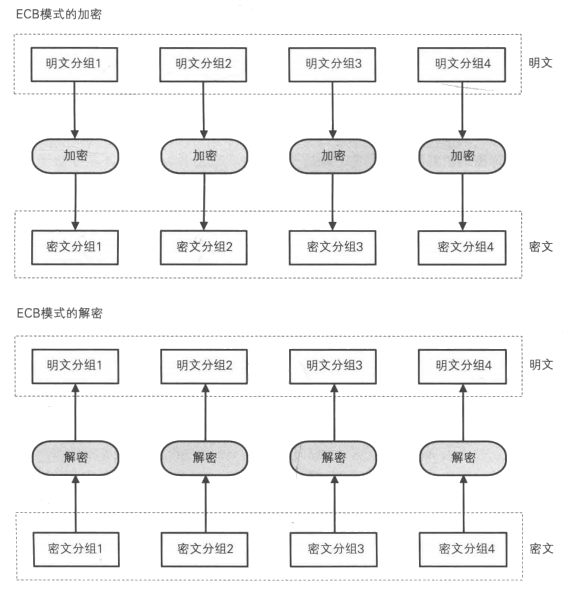
- Electronic Code Book (ECB): Each block encrypted separately
电子密码本(ECB):每个块单独加密
在ECB模式中,明文加密之后将直接得到密文,同样的密文解密之后,也直接得到明文。明文长度必须是“分组长度”的整数倍,非整数倍的,需在加密之前将其填充为“整数倍”
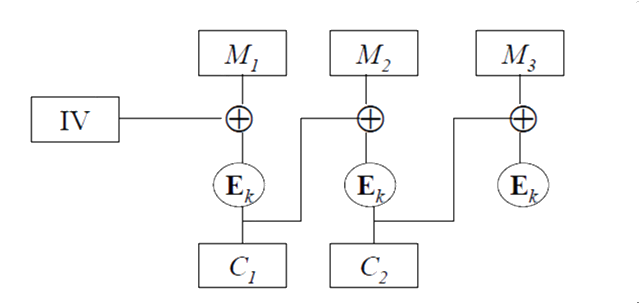
- Cipher Block Chaining (CBC): Next input depends on previous output 密码块链接(CBC):下一个输入取决于前一个输出
- Electronic Code Book (ECB): Each block encrypted separately
电子密码本(ECB):每个块单独加密
- CRYPTOSYSTEM: (or Cryptographic system) is the package of all procedures, protocols, cryptographic algorithms and instructions used for enciphering and deciphering messages using cryptography. 密码系统(Cryptosystem 或 Cryptographic system):指通过使用密码学进行加密和解密消息的所有程序、协议、密码算法和指令的集合
- CHOOSING ALGORITHMS
- Depends on the application
- Encrypting streams of data in real-time has different requirements than encryption files on your local computer 实时加密数据流的需求与加密本地计算机上的文件不同
- SYMMETRIC: Best for data on your hard drive 对称加密:最适合硬盘上的数据
- PUBLIC: Good for communication (messages) 公钥加密:适合通信(消息)
- Depends on the application
- Cryptography is Used to Achieve Information
- CONFIDENTIALITY: only authorized persons can access/read information 只有授权人员可以访问/读取信息
- INTEGRITY: Information that was sent is what was received 接收到的信息与发送的信息一致
- AUTHENTICATION: Guarantee of originator and of electronic transmission (using digital signature) 保证发送者的身份以及电子传输的真实性(使用数字签名)
- NON-REPUDIATION: Originator of information cannot deny content or transmission (using digital signature) 信息的发送者不能否认内容或传输行为(使用数字签名)
![[Pasted image 20250402125311.png#pic_75center|]]